Medical team
Our team is at your service to guide you through an important path aimed to shift your teeth and jaw to a more balanced position, merging aesthetics with functionality.
Orthognathic surgery?
People who can benefit from orthognathic surgery are those who suffer from mastication problems which cannot be improved with classic orthodontics and those whose dental arches are misplaced because of jaw growth discrepancies.
Contacts
Ortognatica Roma – Assunzione di Maria Sant.ma Clinic Center, Via Nomentana 311, 00198 Rome.
To book an appointment, please call
+39 351 504 0117
Orthognathic surgery
The aim of orthognathic surgery is to achieve facial harmony: the main purpose of these surgical procedures is to correct a wide variety of craniomaxillofacial defects through mandibular/maxillary surgery in order to achieve the perfect balance between all facial features of the patient. Orthognathy not only allows the correct positioning of the dental arches in order to treat occlusion defects, but it also offers significant aesthetic results combined with functional improvements on breathing, mastication, phonation and posture. As a branch of maxillofacial surgery, orthognathy can correct several dentofacial deformities
such as maxillary or upper jaw excess or deficiency, facial asymmetries, open bite, underbite as well as crossbite which cause malocclusion problems. The dentoskeletal alterations during growth are often minimal and thus are included in the canons of normal human anatomy but there are some cases in which these defects are pronounced and can cause temporomandibular joint problems associated with premature loss of the affected teeth. Behind an evident aesthetic problem, there are always functional implications that should not be underestimated.
The main defects that can be corrected thanks to orthognathic surgery are:
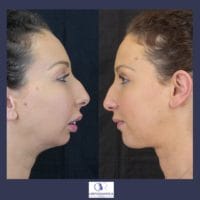
1. Dentoskeletal class II (small chin)
and underdeveloped jaw, receding chin, presence of a wide gap between upper and lower incisors.

2. Dentoskeletal class III (long chin)
and excessive growth of the lower part of the face characterized by an excessively large or pronounced jaw, mandibular prognathism and possible presence of crossbite.

3. Aentofacial asymmetries
More or less evident dentofacial asymmetries with mandibular, chin and upper jaw deviations.
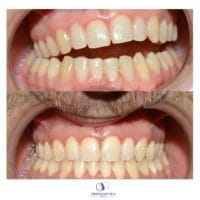
4. Alterations of occlusion which are not correctable with classic orthodontics:
deep bite, crossbite, open bite.
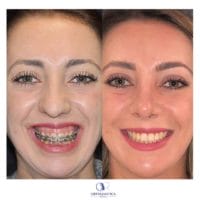
5. Gingival smile, the so-called “Gummy Smile”
with excessive gingival display.
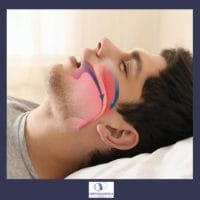
6. Sleep apnea syndrome (OSA)
severe obstructive
Orthognathic surgery phases

Phase 1
Online pre-operative visit

Phase 2
Pre-surgical planning

Phase 3
Pre-surgical orthodontics

Phase 4
Aesthetic and functionality in orthognathic surgery
Phase 5
Surgical operation
Phase 6
Postoperative care

